Jump To:
Pneumatic vs Electric Tools
Understanding the differences, applications, and benefits of electric and pneumatic tools is crucial for anyone trying to pick the right-hand tools to complete a job efficiently and effectively.
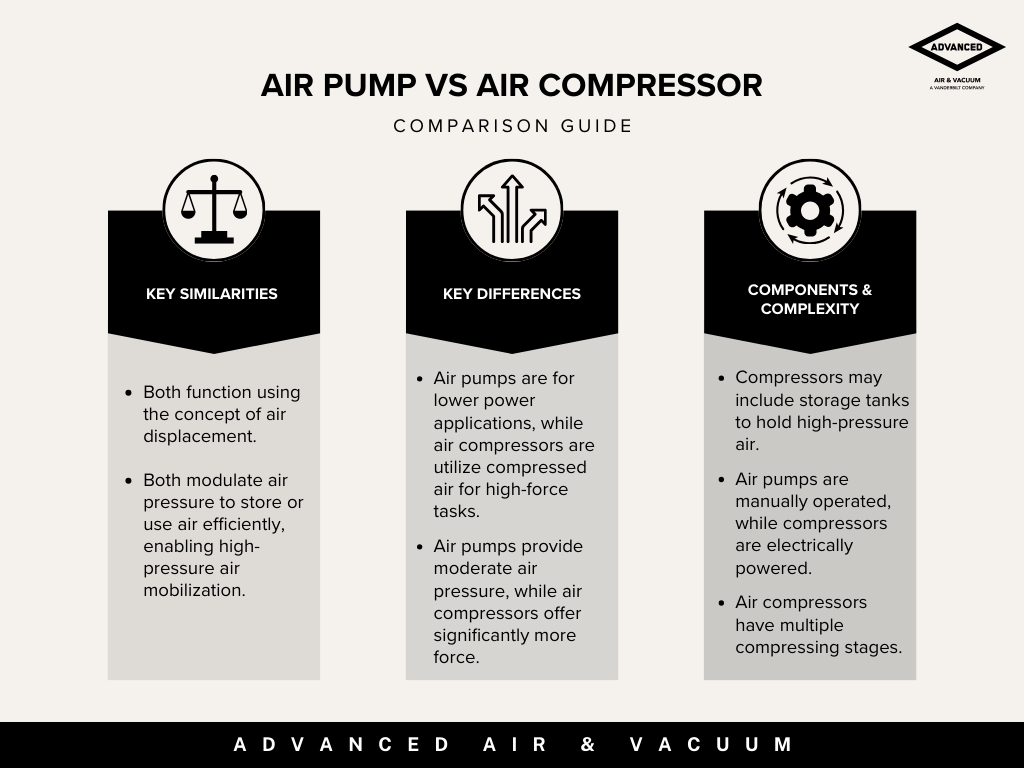
TL;DR: Pneumatic tools, also known as air-powered tools, rely and run on pressurized gas generated by an air compressor. Consider the experience of using a spray paint can: the pressurized air inside propels the paint out in a steady, powerful stream. Similarly, an air compressor powers pneumatic tools, enabling them to perform tasks such as powering a nail gun or operating an impact wrench. On the other hand, electric or battery tools depend on a power source to function, whether they are plugged into an outlet or use a battery.
There are advantages and disadvantages to every power tool and choosing between pneumatic and electric tools depends on the specific requirements of your work.
Pneumatic vs. Electric Tools: A Breakdown
When deciding between pneumatic and electric tools for a project, understanding their strengths, cost implications, application performance, and handling can guide you to the right choice. Each tool brings its own set of benefits and limitations, shaping how you will use them in various tasks.
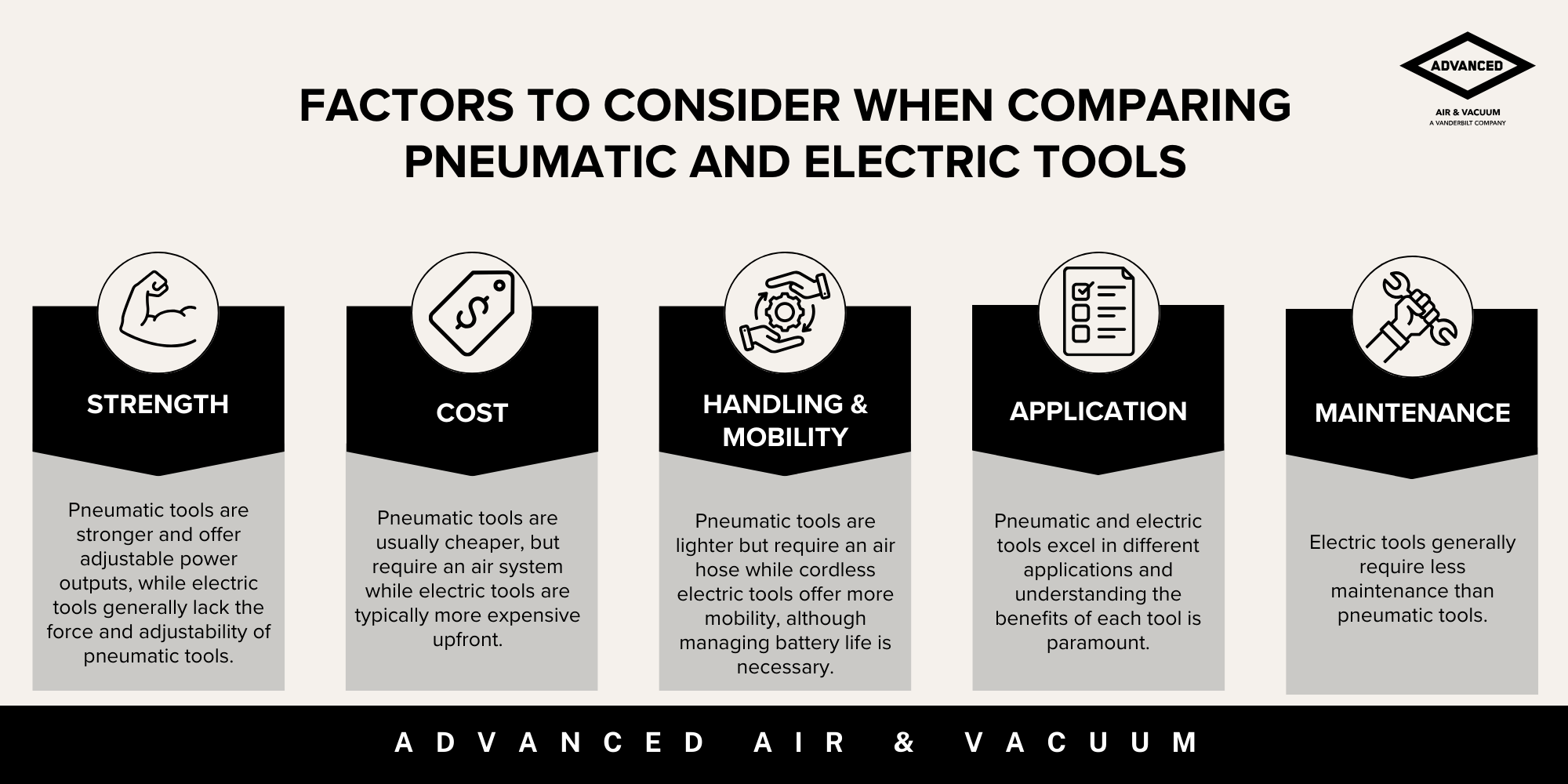
Strength
Pneumatic tools are typically stronger than most electric tools and stand out for their ability to adjust their power output. On the other hand, electric tools have made significant strides in power and efficiency in recent years. Though they’ve become more potent, they generally cannot match the sheer force of pneumatic tools, and most cannot adjust power output.
Cost
Pneumatic tools are often less expensive than their electric counterparts. However, the need for an air compressor for an air-powered tool can substantially add to the initial investment. Electric tools, while typically more expensive for the tool alone, do not require the added expense of a pneumatic system, making them a more cost-effective choice for those without an existing compressor setup.
Handling and Mobility
One notable difference in handling is the weight; pneumatic tools are generally lighter than electric tools, which can significantly impact fatigue over long periods of use. Additionally, considering the potential for cordless electric tools is another factor to consider. Battery-powered tools offer freedom of movement compared to being tethered by an air hose, though this mobility comes at the cost of having to manage battery life and power limitations.
Application Performance
Pneumatic and electric tools each excel in specific applications. Certain tasks, such as airbrushing, inflating tires, or driving nails, are uniquely suited to pneumatic tools. Meanwhile, electric tools are favored for their convenience and portability, particularly in settings without easy access to an air compressor, such as remote job sites, home workshops, or when working at heights where using an air compressor would be impractical or unsafe.
Maintenance
When comparing maintenance time between pneumatic and electric tools, electric tools generally require less maintenance. While pneumatic tools need periodic checks and inspections, electric tools typically have fewer moving parts and do not rely on external air sources, reducing the need for frequent maintenance tasks.
Some tools have an electric model and a pneumatic counterpart, and your choice between the two comes down to many considerations. For instance, when comparing a pneumatic drill to an electric drill or a pneumatic impact wrench to an electric impact wrench, the choice often boils down to the specific needs of the task and the user’s preference. Whether it’s the unmatched strength and adjustability of pneumatic tools or the convenience of electric tools, understanding these aspects will help you make an informed choice that enhances your work efficiency and performance.
Types of Pneumatic Tools and Their Uses
Let’s look at some of the most common pneumatic tools and their applications:
Pneumatic Drills
Pneumatic drills are ideal for drilling through materials like metal, wood, and plastic with ease. They are often used in heavy-duty applications where speed, power, and accuracy are paramount.
Nail Guns and Staplers
Pneumatic nail guns drive nails into wood or other materials quickly and securely, making tasks like framing and roofing faster and more efficient. Staplers work similarly, perfect for attaching materials with high precision. These powerful tools are staples in construction and woodworking.
Air Brushes
These tools are used for applying paint, stains, and varnishes in a fine mist, allowing for precision and uniform application over surfaces. Airbrushes are popular in automotive painting, model-making, and artistic projects.
Tire Inflators
A practical and essential tool for maintaining optimal tire pressure, pneumatic tire inflators are easy to use and provide accurate pressure adjustments, ensuring vehicle safety and efficiency.
Each pneumatic tool offers unique advantages for specific tasks, making them invaluable assets in various industries and hobbies. Understanding the capabilities and uses of these tools can help you select the right pneumatic equipment for your project, ensuring quality results and efficient work processes.
Types of Electric Tools and Their Uses
Electric tools are indispensable in both professional settings and home workshops for their versatility and ease of use. Each electric tool is engineered to tackle specific tasks, enhancing efficiency and effectiveness. Here are some of the most common electric tools and their applications:
Electric Drills
Electric drills are versatile tools capable of drilling holes and driving screws into various materials, including wood, metal, and plastic. With a range of attachments, they can also be used for sanding, grinding, and even mixing paint, making them a great tool for at-home garages and in professional settings alike.
Saws
From circular saws for cutting straight lines through wood to jigsaws for curved cuts and reciprocating saws for demolition work, electric saws enable precise cuts in a variety of materials, making them indispensable tools for construction, renovation, and creative projects.
Electric Sanders or Polishers
Electric sanders are designed for smoothing surfaces efficiently and they’re ideal for preparing wood for painting or varnishing, removing rust from metal, or finishing drywall. Electric polishers are used to buff and polish surfaces to a high shine. They’re commonly used on cars, boats, and woodworking to achieve a smooth, glossy finish on paint, metal, or wood.
Other
Electric tools extend to many other devices, including heat guns for stripping paint and welding plastics or leaf blowers and trimmers for garden maintenance, and each tool offers unique benefits, catering to specific tasks and projects. Electric tools bring convenience and precision to a wide range of jobs, from construction and maintenance to crafting and home improvement, and understanding the varied types of tools and their uses helps you equip your workspace with the right tools to tackle any project.
Choosing the Right Tools
When selecting between pneumatic and electric tools, it’s essential to recognize that there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Each type of tool has its own set of advantages and considerations, and the decision you make depends on several factors.
Firstly, the power requirements for your tasks are crucial; pneumatic tools often provide high torque and adjustable power, perfect for heavy-duty, precision tasks. Secondly, the cost factor plays a role; pneumatic tools might be less expensive upfront compared to electric ones, but remember to account for the air compressor’s cost, which can significantly impact the initial investment. Lastly, the nature of the tasks and handling needs should guide your choice; pneumatic tools are unparalleled for tasks demanding power and precision, whereas electric tools offer superior convenience and portability for jobs requiring ease of movement.
Both pneumatic and electric tools have their benefits and drawbacks, and making an informed decision requires careful consideration of your specific needs and preferences. For installation, repair, or maintenance on your compressed air system or to better understand whether pneumatic or electric tools are best suited for your specific applications, reach out to us at Advanced Air & Vacuum. Our team of experts is here to provide guidance and support to ensure you have the right tools for the job.