Table of Contents
If you’re tasked with managing or installing a compressed air system, you know that determining the correct pipe size is one of the most crucial steps in the process. But how do you find the perfect fit?
The Short Answer: To size compressed air pipes correctly, you need to consider the compressor output, demand of your air-powered tools or pneumatic equipment, pressure requirements, and the length of the pipe. It’s also crucial to consider future needs if your system expands down the line; larger pipes may serve you better in such cases. But it’s not just about the diameter of the pipe. The material of the pipe, like aluminum, black iron, or stainless steel, can also factor into the calculation, impacting flow rate, energy consumption, and overall system performance.
In this post, we’ll dive deeper into the specifics, breaking down each of these elements in detail to help you navigate the process and avoid issues like pressure loss, friction loss, and unnecessary energy costs. Whether you’re dealing with an intricate distribution network or a simple compressor outlet, you’ll have a solid grasp on compressed air pipe sizing by the end of this comprehensive guide.
Understanding Compressed Air and Its Importance Across Industries
Compressed air can be considered as the fourth utility, following electricity, water, and natural gas. It is essentially air that is pressurized, stored in a confined space, and then harnessed as a powerful source of energy for a multitude of applications.
Role of Compressed Air in Various Industries
Industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and automotive shops, all rely heavily on compressed air. Whether it’s automotive technicians using air-powered impact wrenches to fasten lug nuts or production lines depending on compressed air for machinery actuation, product movement, or cleaning processes, the applications truly are extensive.
The Connection between Compressed Air & Air Compressors
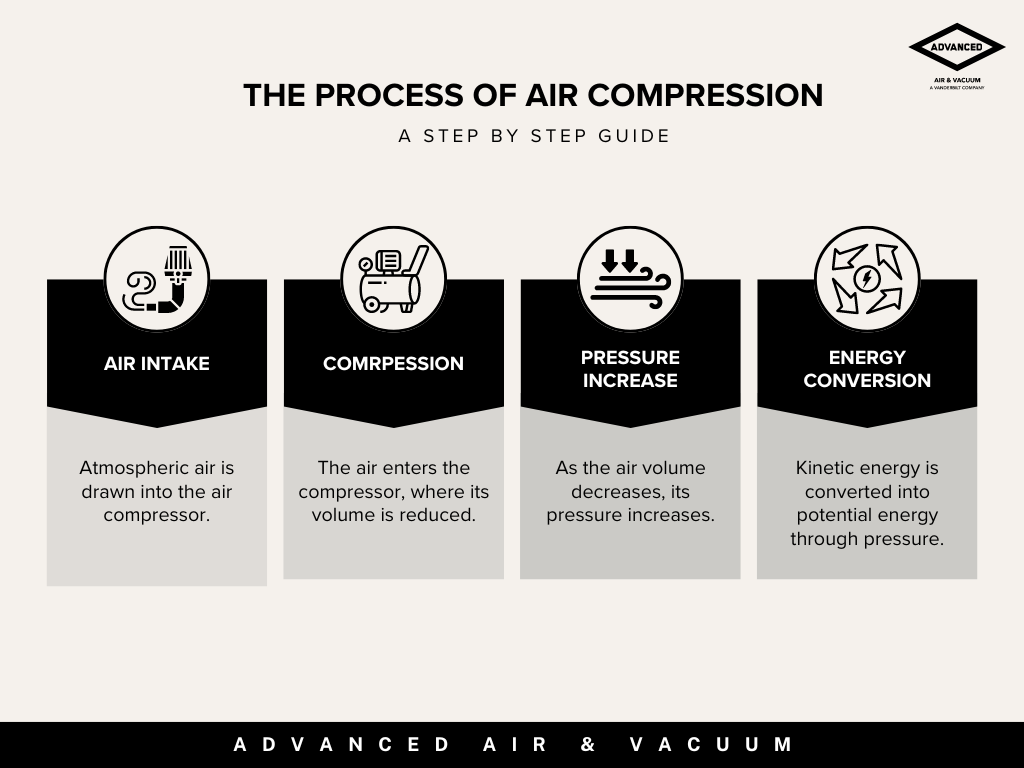
The air compressor is the core of any compressed air system. Functioning as the system’s heart, it draws in ambient air, compresses it into a smaller volume, and then pushes it into the pipe network at an increased pressure. Simply put, the compressor is responsible for maintaining the life force of your air system.
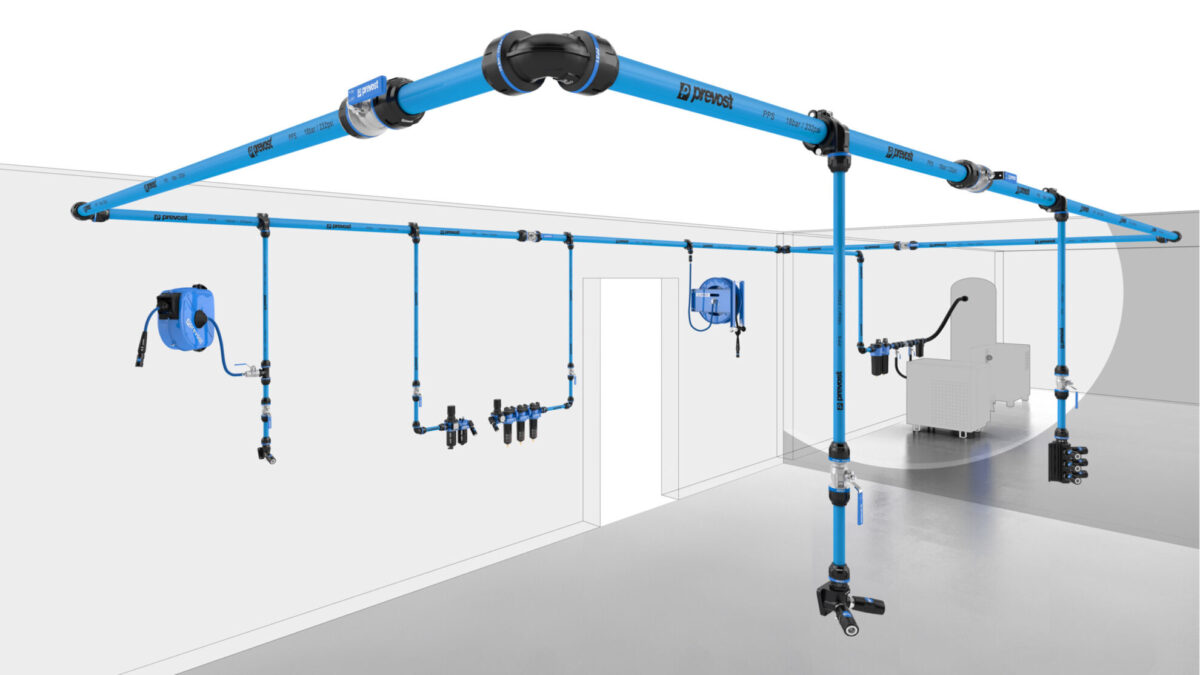
The Significance of Pipe Sizing in Compressed Air Distribution
This brings us to the crucial role pipe sizing plays in ensuring your compressed air system operates effectively. Efficient airflow from the compressor to the end-user is dependent on selecting the correct air pipe size. A pipe that’s too narrow can induce a significant pressure drop, while an unnecessarily large pipe could lead to both decreased pressure and increased installation and energy costs.
Key Factors in Compressed Air Pipe Sizing
Understanding the Role of Pressure Drop
The term ‘pressure drop’ can be seen as the enemy of any air system. It denotes the difference in pressure from the compressor outlet to the point of use. A significant pressure drop may lead to inefficiencies in your air system, as your compressor needs to work harder to normalize the pressure, thereby wasting energy. Recognizing the link between pipe sizing and pressure drop – namely, factoring pipe size to keep pressure drop to an acceptable level – is crucial for efficient operation.
Importance of Flow Rate
Flow rate is another important determinant in air pipe sizing. Simplified, it’s the quantity of air moving through the pipe at one time. The flow rate will depend on the demand of your air-powered tools or pneumatic equipment. A higher flow rate could necessitate a larger pipe to maintain pressure and avoid overloading your compressor.
Implications of Pipe Diameter
The inner diameter of the pipe directly impacts both pressure and flow rate in the system. A narrow path slows down air flow and leads to high pressure. Conversely, a larger pipe creates more space for air, reducing pressure but allowing for greater air velocity.
Smaller Pipes vs Larger Pipes
It’s not always that larger is better, particularly with pipe sizes. Bigger pipes may seem more efficient in terms of airflow and pressure, but they can also increase your energy consumption and installation costs. Conversely, smaller pipes might reduce costs but can cause pressure drop and affect compressor output. Understanding the balance here is key.
Considering Pipe Length
Longer pipes add more friction, potentially reducing the flow rate and causing pressure drop. Hence, the total pipe length, including main lines and branch lines, is fundamental while making pipe size decisions.
Future Expansion
Remember to incorporate room for growth in your system, particularly if you anticipate future expansion. It’s more cost-effective to install a bit larger pipes now than to suffer pressure drop down the line.
Choosing the Right Materials for Your Compressed Air Pipes
Beyond simply the dimensions, pipe material is another pivotal element in compressed air pipe sizing. Let’s look at three of the most commonly selected materials – stainless steel, aluminum, and black iron.

The Role of Stainless Steel
Stainless steel pipes, with their corrosion resistance, are an excellent choice for certain sensitive applications. They help maintain clean compressed air which can be crucial for applications like the medical or food processing industries. However, they come with a heftier price tag compared to other materials.
Advantages of Aluminum Pipe
Aluminum pipes are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and easy to install. They often work well in both small businesses and larger industrial settings where the ease of modifying the distribution network is a valuable feature.
Utilizing Black Iron Pipes
Black iron, while budget-friendly, is more susceptible to corrosion and can affect the quality of your compressed air. However, they can be a suitable choice in environments where the air quality is not highly critical.
Pipe Material & Energy Consumption
Why does the material matter? It’s all about the smoothness of the pipe’s interior surface. Smoother surfaces decrease friction loss, which in turn reduces the compressor’s energy consumption and operating costs. By choosing a material like aluminum or stainless steel, known for smoother interiors, you’re enhancing your compressed air system’s energy efficiency.
The Role of Advanced Air & Vacuum in Compressed Air Pipe Sizing
Selecting the appropriate pipe size for your compressed air system is a calculated decision, requiring accurate measurements, an understanding of the system, and a familiarity with your industry’s requirements. Advanced Air & Vacuum is the go-to choice for businesses in California, Arizona, and Las Vegas looking to get an air system installed.
Beyond setting you up with the perfect air compressor, we offer a full suite of services that include project consultation, system planning, installation, and superior post-install maintenance. Our team collaborates closely with local engineers, plant managers, and other team personnel, ensuring that the equipment supplied for every job is the ideal fit.
The complexity of compressed air pipe sizing should not deter you from achieving an efficient and optimal system. With Advanced Air & Vacuum as your trusted partner, you’re guaranteed top-quality service and satisfaction, no matter the size of your project.
Contact us today to get started making your business safer and more efficient!
 Article written 12/03/2024:
Article written 12/03/2024: With over 15 years of experience, Joseph is an expert in air compressor equipment, vacuum pumps, and pneumatic systems, possessing a unique blend of technical knowledge and practical skills. As a pneumatic system energy auditor and designer, he is proficient in diagnosing system inefficiencies, optimizing performance, and designing tailored solutions to meet clients' needs.
See more See less

